RADCamp NYC 2019 Part II (Bioinformatics)
Day 1 (AM)
Overview of the morning activities:
- Welcome and participant intro slides
- Intro to RADSeq (Brief)
- Intro to ipyrad documentation
- Connect to a binder instance
- RADseq data quality control (QC)
- ipyrad CLI assembly of simulated data Part I
Participant intros part I
1 minute/1 slide participant intros
Brief intro to RADSeq
Lead: Deren Introduction to RAD and the terminal
Intro ipyrad docs
Intro to binder
We will perform the basic assembly and analysis of simulated data using binder, to launch a working copy of the ipyrad github repository. The binder project allows the creation of shareable, interactive, and reproducible environments by facilitating execution of jupyter notebooks in a simple, web-based format. More information about the binder project is available in the binder documentation.
NB: The binder instance we will use here for the first day is a service to the community provided by the binder project, so it has limited computational capacity. This capacity is sufficient to assemble the very small simulated datasets we provide as examples, but it is in no way capable of assembling real data, so don’t even think about it! We use binder here as a quick and easy way of demonstrating workflows and API mode interactions without all the hassle of going through the installation in a live environment. When you return to your home institution, if you wish to use ipyrad we provide extensive documentation for setup and config for both local installs and installs on HPC systems.
NB: Binder images are transient! Nothing you do inside this instance will be saved if you close your browser tab, so don’t expect any results to be persistent. Save anything you generate here that you want to keep to your local machine.
Get everyone on binder here: Launch ipyrad with binder.

Have patience, this could take a few moments. If it’s ready, it should look like this:
Data QC: Fastq format and FastQC
Lead: Laura
Each grey cell in this tutorial indicates a command line interaction.
Lines starting with $ indicate a command that should be executed
in a terminal connected to the Habanero cluster, for example by copying and
pasting the text into your terminal. Elements in code cells surrounded
by angle brackets (e.g.
## Example Code Cell.
## Create an empty file in my home directory called `watdo.txt`
$ touch ~/watdo.txt
## Print "wat" to the screen
$ echo "wat"
wat
To start the terminal on the jupyter dashboard, choose New>Terminal.
Here we’ll use bash commands and command line arguments. If you have trouble remembering the different commands, you can find some very usefull commands on this cheat sheet. Take a look at the contents of the folder you’re currently in.
$ ls
There are a bunch of folders. To keep things organized, we will create a new directory which we’ll be using during this Workshop. Use mkdir. And then navigate into the new folder, using cd.
$ mkdir ipyrad-workshop
$ cd ipyrad-workshop
Fastq format
The first step of any RADSeq assembly is to inspect your raw data to
estimate overall quality. Your input data will be in fastQ format, usually ending in .fq, .fastq,
.fq.gz, or .fastq.gz. The file(s) may be compressed with gzip so that they
have a .gz ending, but they do not need to be.
We begin first with a visual inspection, but of course we can only visually inspect a very tiny proportion of the total data.
For this exercise we will use one sample from an Anolis dataset
generated by Prates et al. 2016 (single-end GBS). We will download some of these data, using the command wget. Make sure that you are in the ipyrad-workshop folder you just created.
$ wget https://github.com/radcamp/radcamp.github.io/raw/master/NYC2019/data/anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Now, we will use the zcat command to read lines of data from this file and
we will trim this to print only the first 20 lines by piping the output to the
head command. Using a pipe (|) like this passes the output from one command to
another and is a common trick in the command line.
Here we have our first look at a fastq formatted file. Each sequenced read is spread over four lines, one of which contains sequence and another the quality scores stored as ASCII characters. The other two lines are used as headers to store information about the read.
$ zcat anolis_R1_.fastq.gz | head -n 20
@D00656:123:C6P86ANXX:8:2201:3857:34366 1:Y:0:8
TGCATGTTTATTGTCTATGTAAAAGGAAAAGCCATGCTATCAGAGATTGGCCTGGGGGGGGGGGGCAAATACATG
+
;=11>111>1;EDGB1;=DG1=>1:EGG1>:>11?CE1<>1<1<E1>ED1111:00CC..86DG>....//8CDD
@D00656:123:C6P86ANXX:8:2201:5076:34300 1:N:0:8
TGCATATGAACCCCAACCTCCCCATCACATTCCACCATAGCAATCAGTTTCCTCTCTTCCTTCTTCTTGACCTCT
+
@;BFGEBCC11=/;/E/CFGGGG1ECCE:EFDFCGGGGGGG11EFGGGGGCGG:B0=F0=FF0=F:FG:FDG00:
@D00656:123:C6P86ANXX:8:2201:5042:34398 1:N:0:8
TGCATTCAAAGGGAGAAGAGTACAGAAACCAAGCACATATTTGAAAAATGCAAGATCGGAAGAGCGGTTCAGCAG
+
GGGGGGGCGGGGGGGGGGGGGEGGGFGGGGGGEGGGGGGGGGGGGGFGGGEGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGG
@D00656:123:C6P86ANXX:8:2201:6052:34481 1:Y:0:8
TGCATCTACACTGTAGAATTAATGTAATTTGACACCACTTTAATTCCCATGGCTCAATGCTATCGGATCCTGGGA
+
GF1FGGG11@1EDGGGG>@11?B1B1=>1@F>C1><00E1FFFECC1CDDG>GGG00=0EG@D0E//E/=F00FB
@D00656:123:C6P86ANXX:8:2201:7303:34463 1:N:0:8
TGCATTTTGCAGTGCAGGCATATTTTGCTAATATCGTGGGGTTAGGACAGGCCCCAGACCACTGTTATAATGCAA
+
GE>@FGFGGCEGGGGGGGFGGGGGGGGGGEGGGGGGGGCBGGGGGGGGGGE0CFGGGGEGBGGGGGFGGCGEGGG
The first is the name of the read (its location on the plate). The second line contains the sequence data. The third line is unused. And the fourth line is the quality scores for the base calls. The FASTQ wikipedia page has a good figure depicting the logic behind how quality scores are encoded.
In this case the restriction enzyme leaves a TGCAT overhang. Can you find this sequence in the raw data?
FastQC for quality control
To get a better view of the data quality, without looking at individual reads, we use automated approaches to check the quality. We will use FastQC to generate a sample-wide summary of data quality.
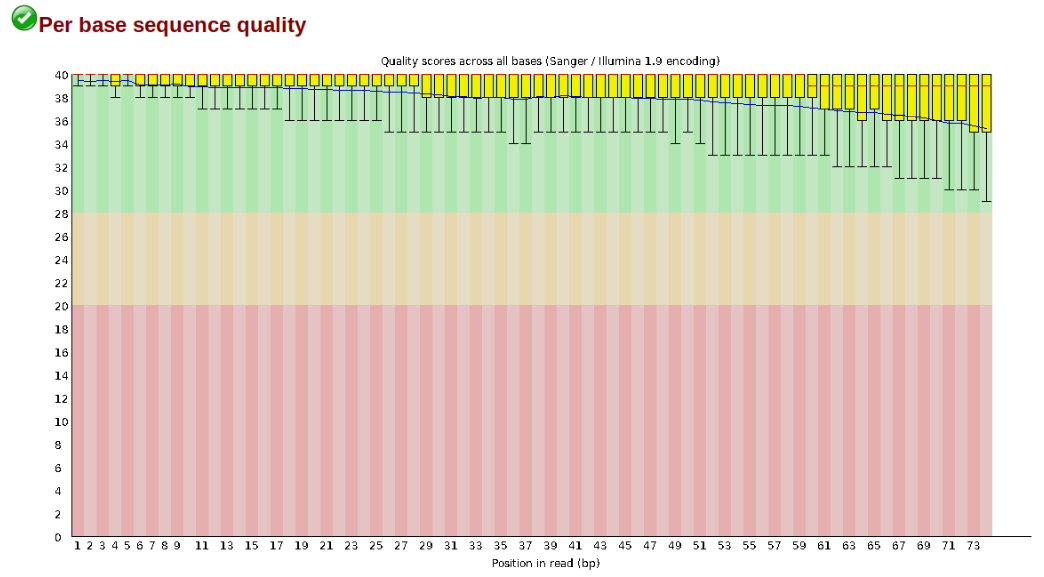
The logic of FastQC is that we want to obtain a high-level view of the quality of the sequencing. You may be able to detect low quality samples, but if you have a lot of samples, you may not want to run FastQC for every single file. Even running it for a few samples will give you good insight into overall quality of the sequencing run. For example, a key QC procedure involves inspecting average quality scores per base position and trimming read edges, which is where low quality base-calls tend to accumulate. In this figure, the X-axis shows the position on the read in base-pairs and the Y-axis depicts information about Phred quality score per base for all reads, including median (center red line), IQR (yellow box), and 10%-90% (whiskers). As an example, here is a very clean base sequence quality report for a 75bp RAD-Seq library. These reads have generally high quality across their entire length, with only a slight (barely worth mentioning) dip toward the end of the reads:
In contrast, here is a somewhat typical base sequence quality report for R1 of a 300bp paired-end Illumina run of ezRAD data:
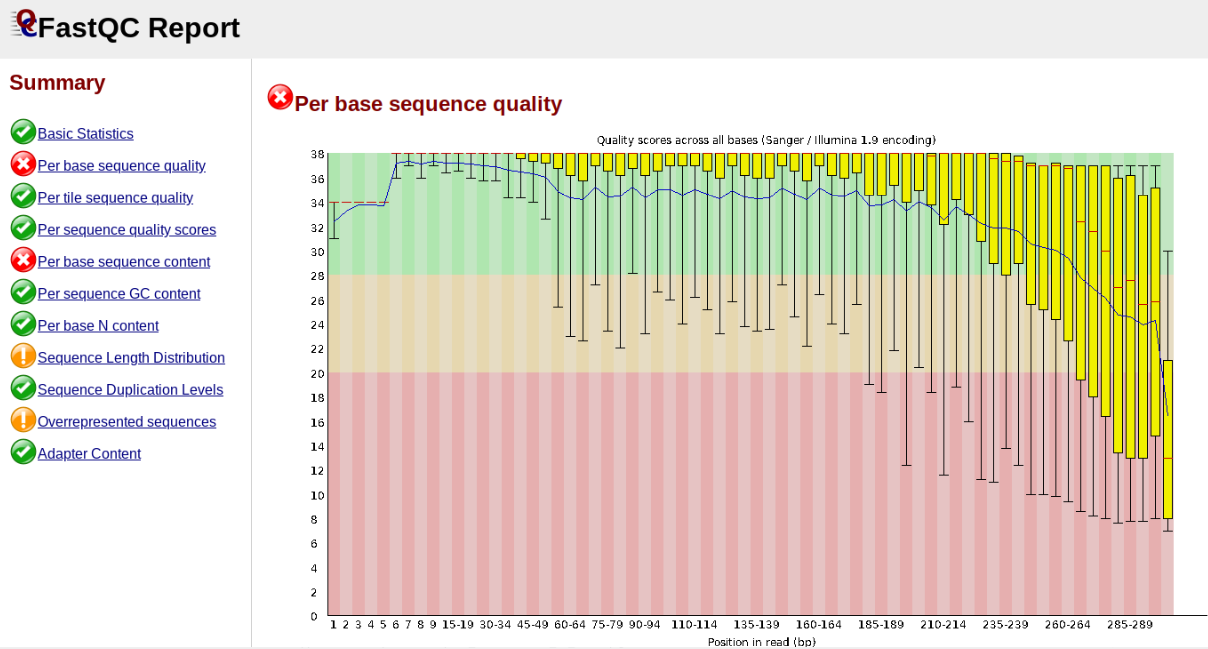
This figure depicts a common artifact of current Illumina chemistry, whereby quality scores per base drop off precipitously toward the ends of reads, with the effect being magnified for read lengths > 150bp. The purpose of using FastQC to examine reads is to determine whether and how much to trim our reads to reduce sequencing error interfering with basecalling. In the above figure, as in most real dataset, we can see there is a tradeoff between throwing out data to increase overall quality by trimming for shorter length, and retaining data to increase value obtained from sequencing with the result of increasing noise toward the ends of reads.
First, install FastQC:
$ conda install -c bioconda fastqc
Type ‘y’ when it asks you if you would like to install other packages (‘Proceed ([y]/n)?’)
Now run FastQC on this sample:
$ fastqc anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
FastQC will indicate its progress in the terminal. This toy data will run quite quickly, but real data can take somewhat longer to analyse (10s of minutes).
Started analysis of anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 5% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 10% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 15% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 20% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 25% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 30% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 35% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 40% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 45% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 50% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 55% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 60% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 65% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 70% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 75% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 80% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 85% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 90% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 95% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Approx 100% complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
Analysis complete for anolis_R1_.fastq.gz
FastQC will save the output as an html file in the folder you’re currently in. You want to look at it in your browser window. So, go back to the jupyter dashboard and navigate to /home/ipyrad-workshop/ and click on
anolis_R1__fastqc.html. This will open the FastQC report which provides
extensive information about the quality of the data, which we will briefly
review here.
Inspecting and Interpreting FastQC Output
Opening up this html file, on the left you’ll see a summary of all the results, which highlights areas FastQC indicates may be worth further examination. We will only look at a few of these.

Lets start with Per base sequence quality.
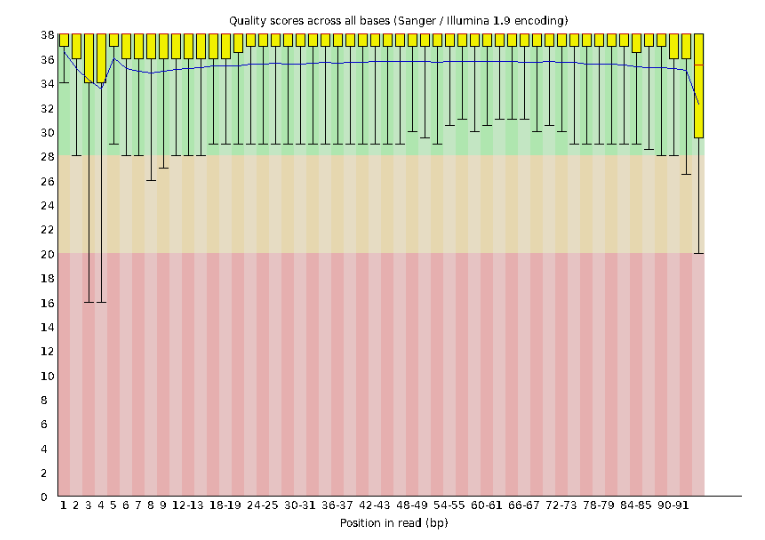
For the Anolis data the sequence quality per base is uniformly quite high, with dips only in the first and last 5 bases (again, this is typical for Illumina reads). Based on information from this plot we can see that the Anolis data doesn’t need any trimming, which is good.
Now lets look at the Per base sequece content, which FastQC highlights with a
scary red X.
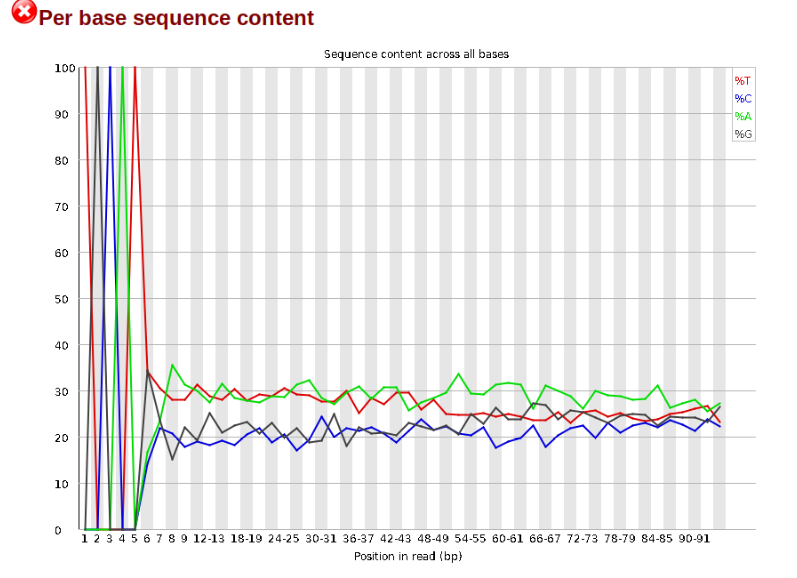
The squiggles indicate base composition per base position averaged across the
reads. It looks like the signal FastQC is concerned about here is related to
the extreme base composition bias of the first 5 positions. We happen to know
this is a result of the restriction enzyme overhang present in all reads
(TGCAT in this case for the EcoT22I enzyme used), and so it is in fact of no
concern. Now lets look at Adapter Content:
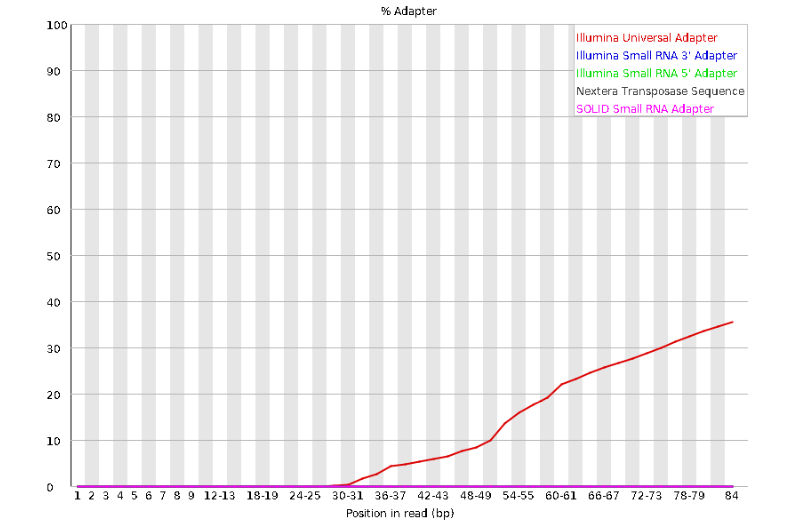
Here, we can see adapter contamination increases toward the tail of the reads, approaching 40% of total read content at the very end. The concern here is that if adapters represent some significant fraction of the read pool, then they will be treated as “real” data, and potentially bias downstream analysis. In the Anolis data this looks like it might be a real concern so we shall keep this in mind during step 2 of the ipyrad analysis, and incorporate 3’ read trimming and aggressive adapter filtering.
ipyrad CLI simulated data assembly Part I
Lead: Isaac
Break for lunch
References
Prates, I., Xue, A. T., Brown, J. L., Alvarado-Serrano, D. F., Rodrigues, M. T., Hickerson, M. J., & Carnaval, A. C. (2016). Inferring responses to climate dynamics from historical demography in neotropical forest lizards. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(29), 7978-7985.